A new paper is added to the collection of reproducible documents: Multi-channel quality factor Q estimation
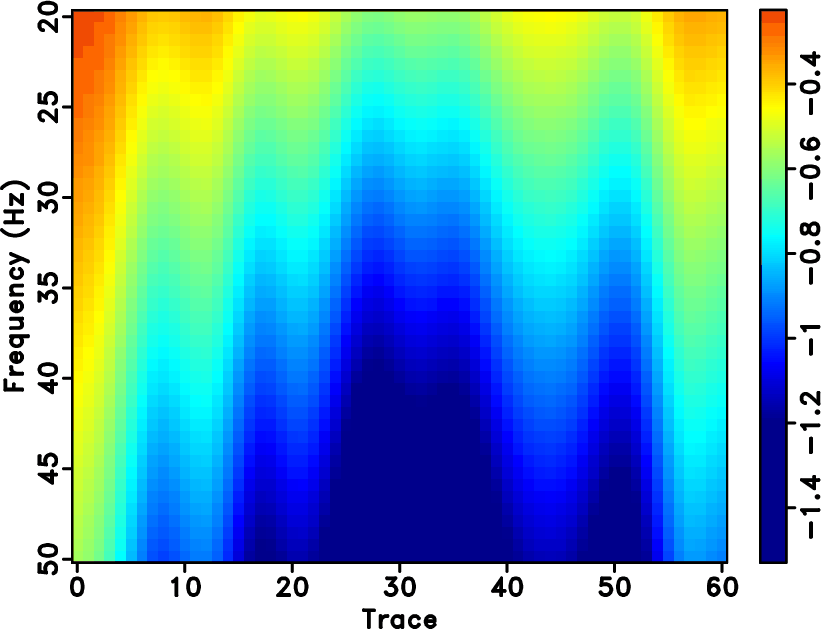
The estimation of quality factor, Q, plays an important role in many geophysical problems, including Q-compensated seismic imaging, geophysical interpretation, and fluid characterization. One of the most widely used approaches for estimating Q is the spectral ratio method (SRM). However, the spectral division in SRM may not be stable due to the spectral nulls. The shaping regularized inversion that treats the spectral division as a regularized least-squares inversion problem can help solve the spectral-nulls problem and make the spectral division stable. In the case of very noisy seismic data, the time-frequency maps can not be optimally obtained and thus the Q estimation performance will be strongly affected and unstable even with the regularized inversion method. We propose a multi-channel Q estimation approach that takes advantage of the multi-channel spatial coherence to constrain the inversion so that the estimated Q is spatially continuous. We use a set of synthetic and real data examples to demonstrate the performance of the multi-channel Q estimation method. Results show that the proposed method can obtain accurate and more importantly stable Q estimation result even in the case of strong random noise.

