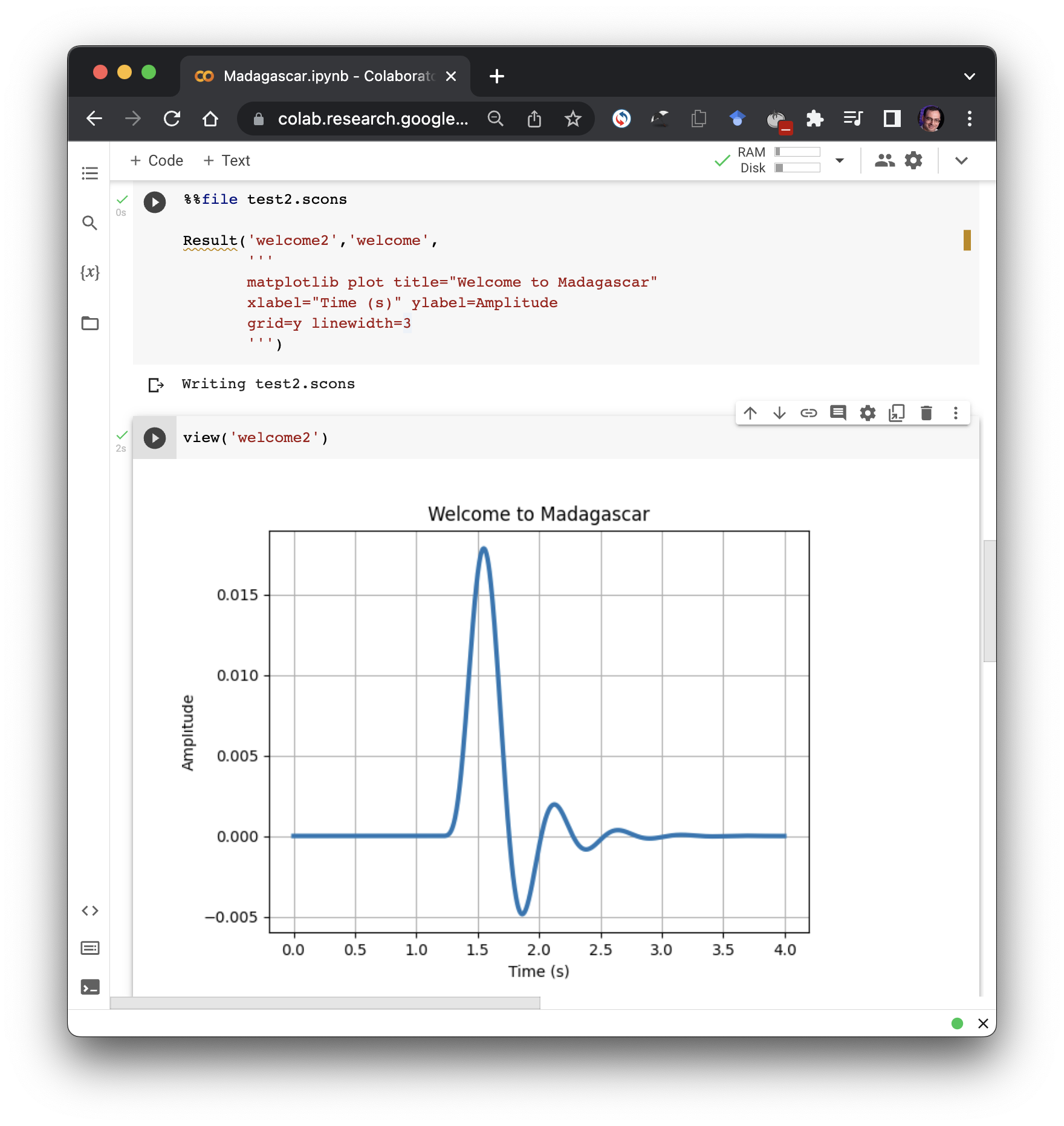
An old paper is added to the collection of reproducible documents: Seismic data interpolation using plane-wave shaping regularization
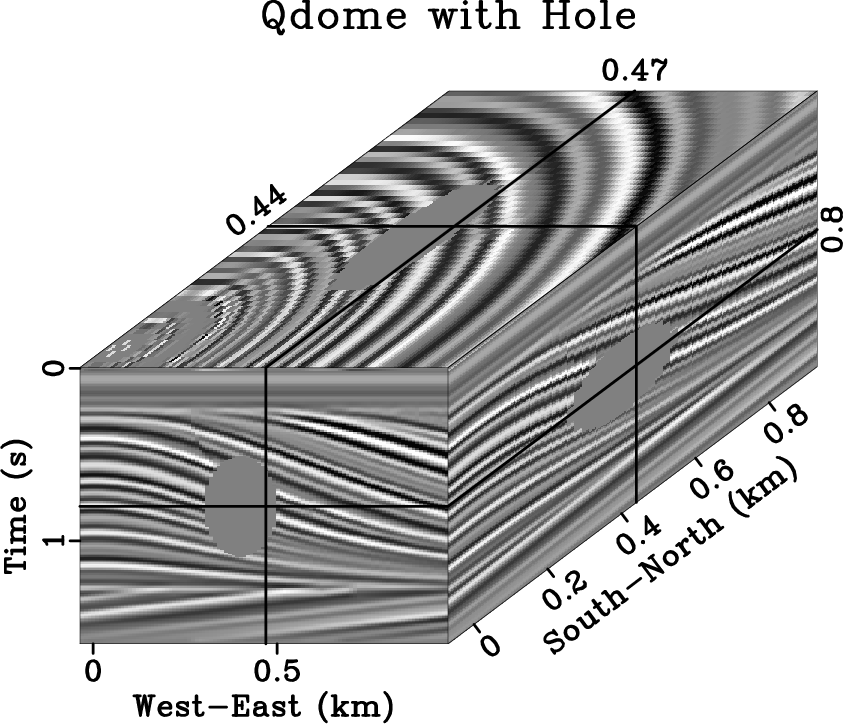
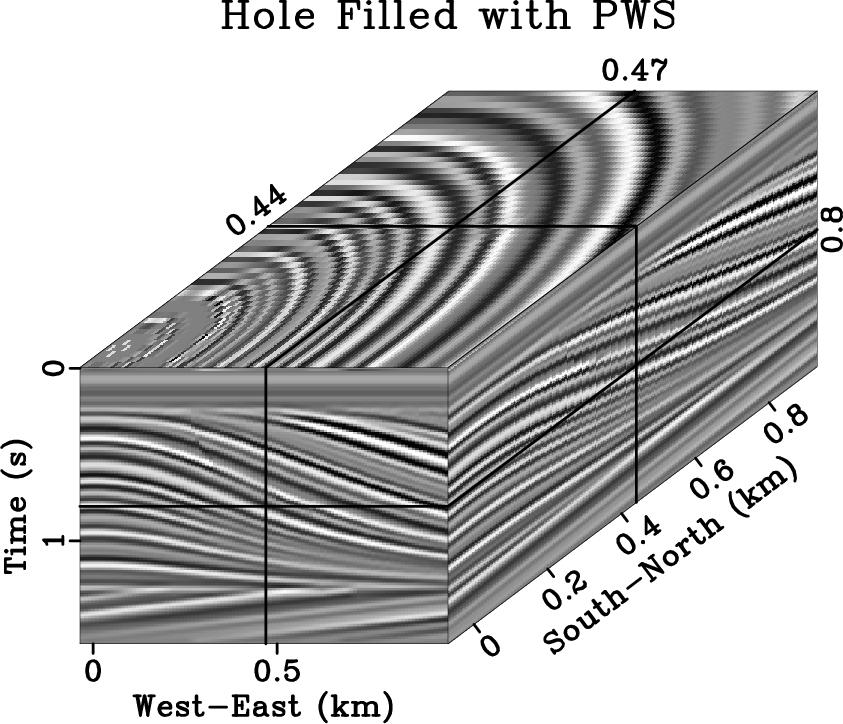
The problem with interpolating insufficient, irregularly sampled data is that there exist infinitely many solutions. When solving ill-posed inverse problems in geophysics, we apply regularization to constrain the model space in some way. We propose to use plane-wave shaping in iterative regularization schemes. By shaping locally planar events to the local slope, we effectively interpolate in the structure-oriented direction and preserve the most geologic dip information. In our experiments, this type of interpolation converges in fewer iterations than alternative techniques. The proposed plane-wave shaping mave have potential applications in seismic tomography and well-log interpolation.