A new paper is added to the collection of reproducible documents:
Automated spectral recomposition with application in stratigraphic interpretation
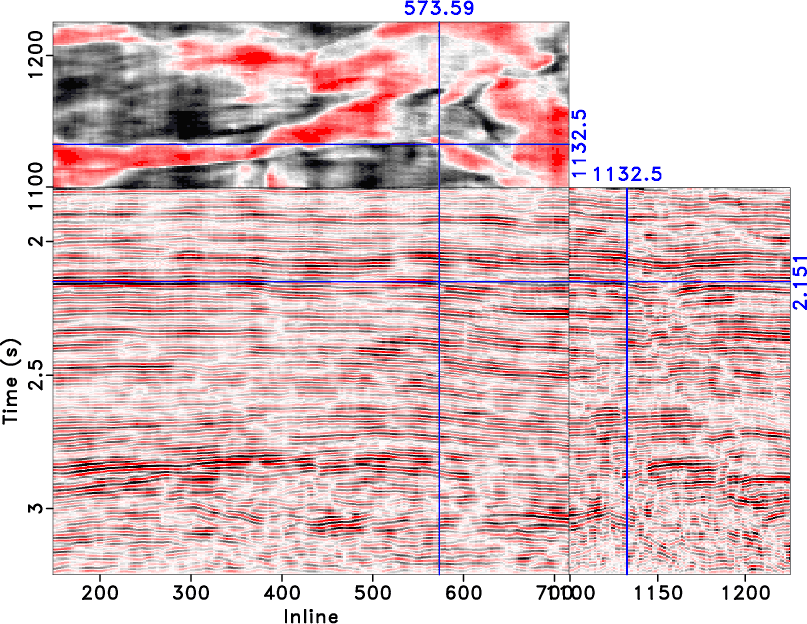
Analyzing seismic attributes in the frequency domain is helpful for reservoir characterization. To analyze the reservoir interval of interest in detail, it is important to capture the seismic response at each frequency subset. Spectral recomposition can be used to extract significant components from the seismic spectrum. We propose a separable nonlinear least-squares algorithm for spectral recomposition, which estimates both linear and nonlinear parts automatically in separate steps. Our approach is applied to estimate fundamental signal parameters, peak frequencies and amplitudes, with which the seismic spectrum can be reconstructed. Automated spectral recomposition helps us visualize frequency-dependent geological features on both cross sections and time slices by extracting significant frequency components. Spectral recomposition can also indicate how frequency contents attenuate with time.
