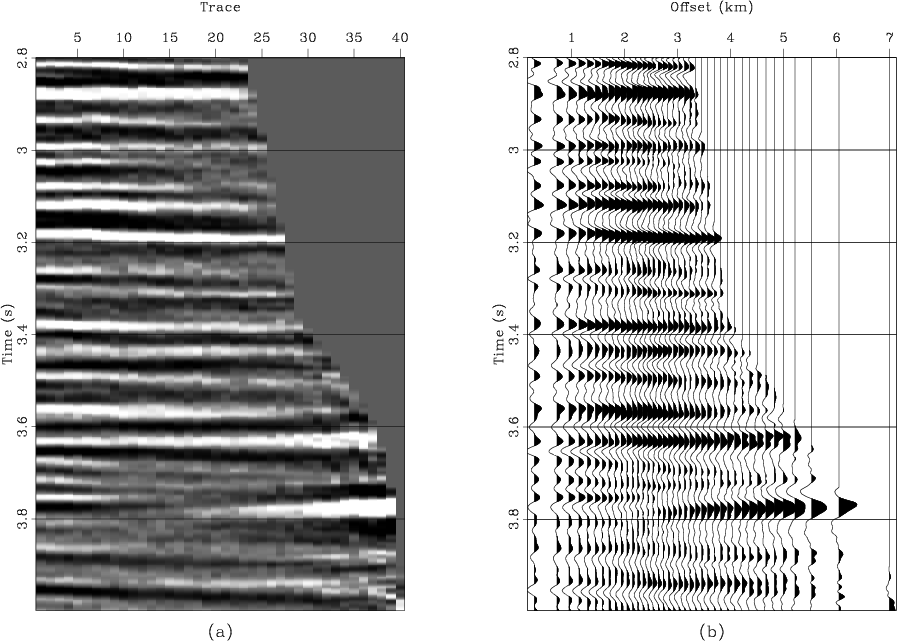
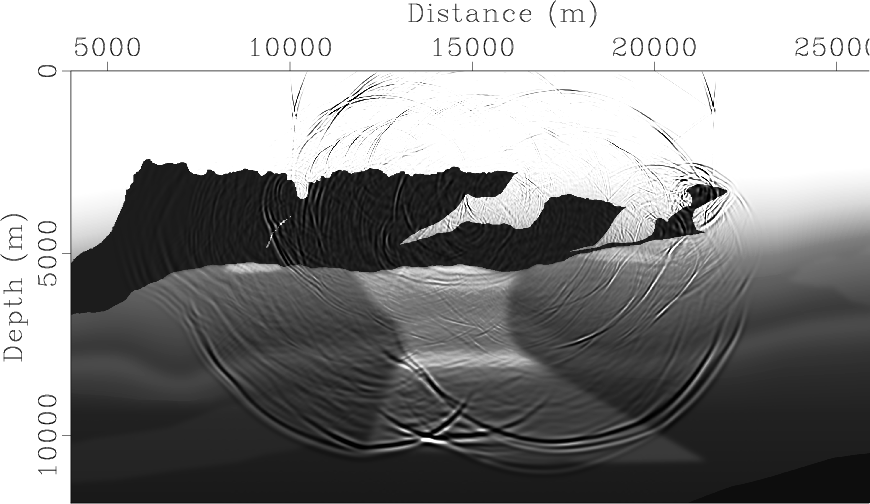
sftime2depth converts the input from vertical time to depth coordinates.
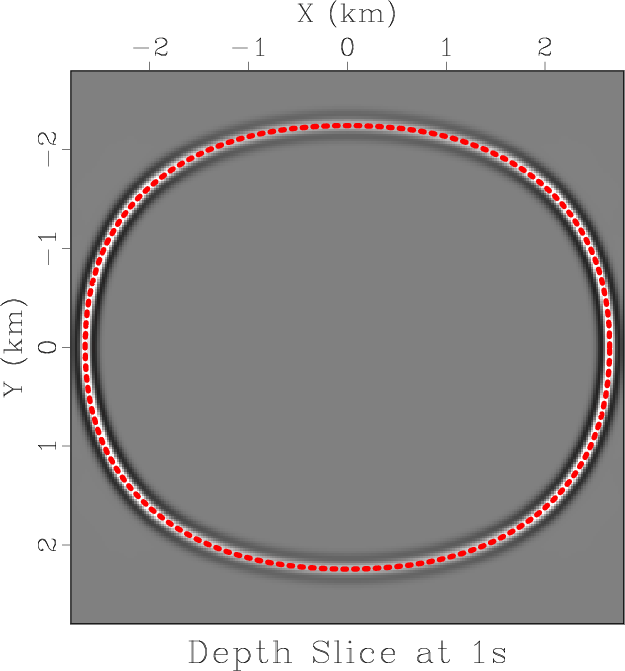
The following example from rsf/su/rsflab9 shows a seismic image converted from time to depth by this transformation:

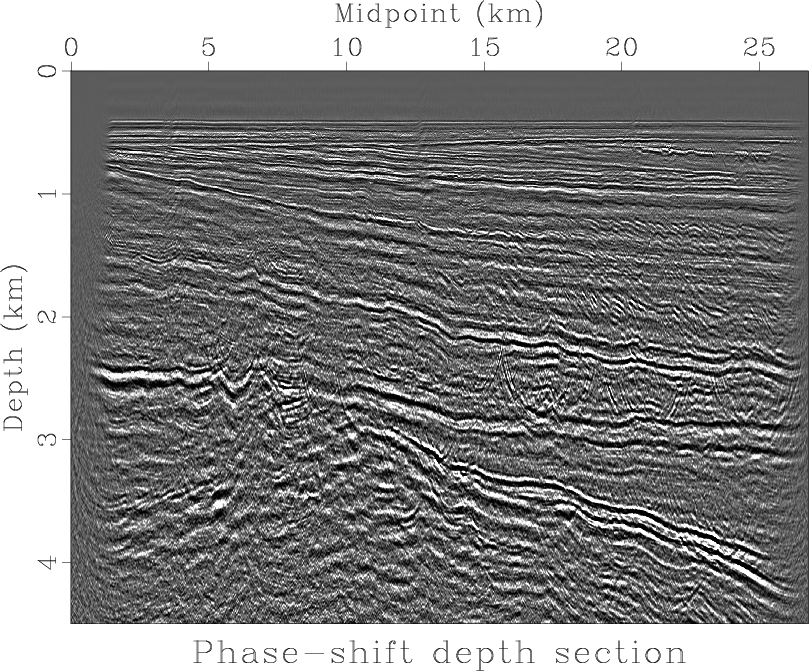
The example is borrowed from John Stockwell’s lecture notes on Geophysical Image Processing and translated from Seismic Unix to Madagascar. The transformation follows the simple equation
$$t = 2\,\int\limits_{0}^{z} \frac{d\zeta}{v(\zeta)}$$,
where $t$ is two-way vertical time, $z$ is depth, and $v(z)$ is vertical velocity.
The sampling of the output depth axis is controlled by nz=, dz=, and z0=. If the velocity (provided in the auxiliary velocity= file) is sampled in time rather than depth, use intime=y. If it is slowness rather than velocity, use slow=y. If the input is in one-way time rather than two-way time, use twoway=n. The interpolation is carried out using B-splines. The spline order is controlled by extend=. By default, cubic splines (extend=4) are used.
The inverse transformation is given by sfdepth2time.
In the presence of lateral velocity variations, the correct transformation from time to depth is not as simple and needs additional corrections. See Time-to-depth conversion and seismic velocity estimation using time-migration velocity.
10 previous programs of the month


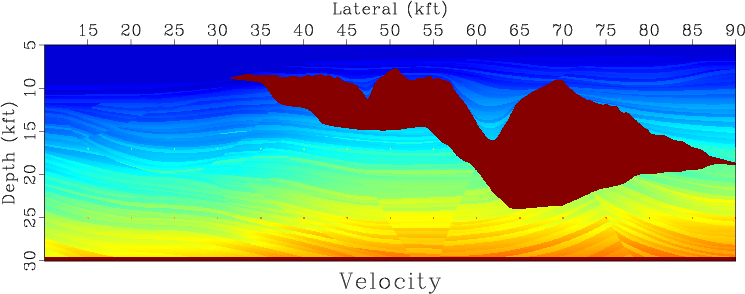
 An unusual experiment in collaborative reproducible research took place in Austin, Texas, on July 25-27: 25 participants from 9 different organizations gathered at the Bureau of Economic Geology, The University of Texas at Austin for the
An unusual experiment in collaborative reproducible research took place in Austin, Texas, on July 25-27: 25 participants from 9 different organizations gathered at the Bureau of Economic Geology, The University of Texas at Austin for the