Starting from this post, once a month we will blog about one of the popular Madagascar programs. The 30 highest ranking programs, according to admin/rank.py, are
grey window math dd spike put graph add cat transp scale pad spray smooth stack noise grey3 real dip ricker1 bandpass dots wiggle mask fft1 segyread contour pick mutter fft3
This month’s randomly selected feature is sfnoise.

As stated in the self-documentation, sfnoise is used for generating random noise and adding it to the data. This is useful for generating synthetic datasets or for multiple realizations in inversion. Computer-generated random numbers are often called pseudo-random, because algorithmically generated sequences of numbers are not truly random. This is actually a useful feature if you want to reproduce previous calculations. For reproducibility, it is imperative to use seed= parameter to set the initial “seed” for the random-number generator. If seed= is not used, it is set by the computer clock. Therefore, different runs of sfnoise will produce different sets of numbers.
Try the following on the command line:
bash$ sfspike n1=5 mag=0 | sfnoise | sfdisfil
0: -2.455 1.197 -0.145 0.2394 0.7676
bash$ sfspike n1=5 mag=0 | sfnoise | sfdisfil
0: 2.203 -0.1106 -0.07494 -0.4916 0.2163
Your sets of numbers will be (most likely) different from the ones above and between the two runs. However, if you run
you should see exactly the same set of number as above. You should also get the same numbers if using
The rep= parameter controls if the noise is replacing the data or being added to the data. The default operation is addition.
The algorithm for pseudorandom number generation that sfnoise uses is known as Mersenne twister. It is a powerful algorithm that generates a nearly uniformly distributed sequence that does not repeat for a very large period of $2^{19937}-1$.
Matsumoto, M.; Nishimura, T. (1998). “Mersenne twister: a 623-dimensionally equidistributed uniform pseudo-random number generator”. ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation 8 (1): 330.
Uniformly-distributed numbers can be used to generate random numbers with other distributions. By default, sfnoise is using normal distribution. It can be changed to uniform distribution by setting type=n.
- See rsf/rsf/sfnoise for simple examples of setting the noise distribution parameters (type=, mean=, var=, range=).
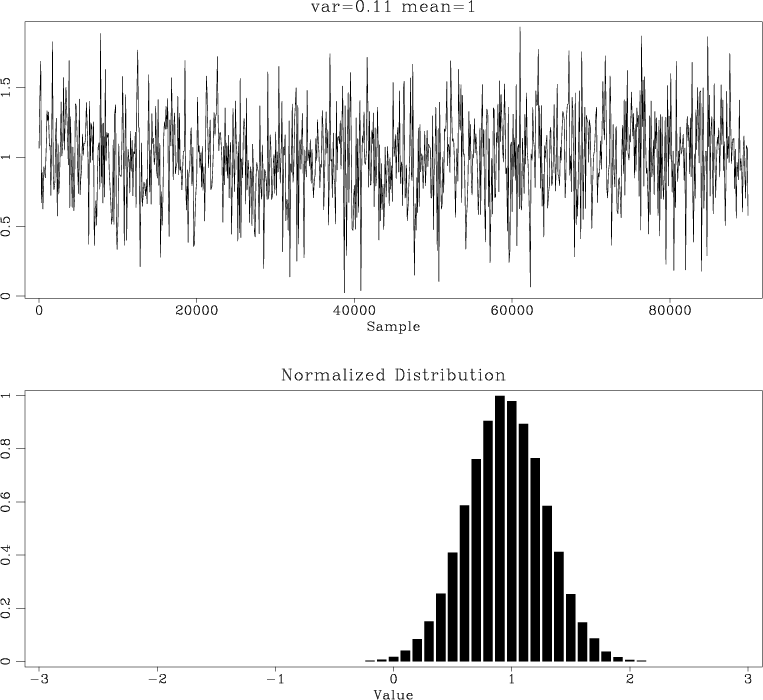

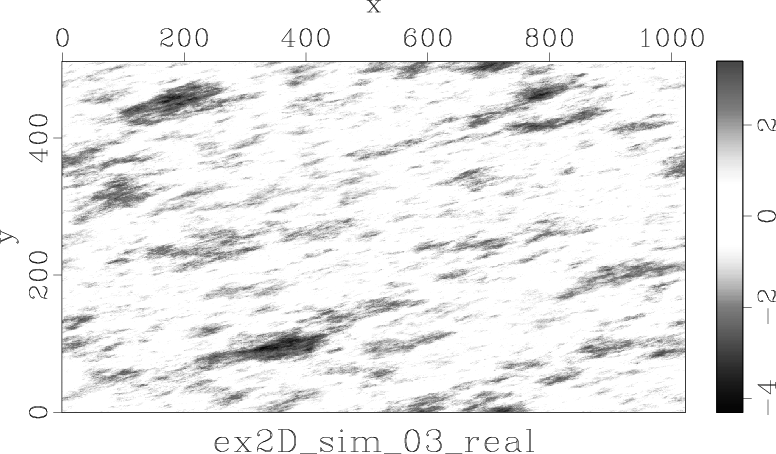
- See geostats/simulate/rfield and Jim Jenning’s presentation at Houston-2010 school for more sophisticated examples of using sfnoise, together with FFT-based variogram computation, in geostatistical simulations.