A new paper is added to the collection of reproducible documents:
Selecting an optimal aperture in Kirchhoff migration using dip-angle images

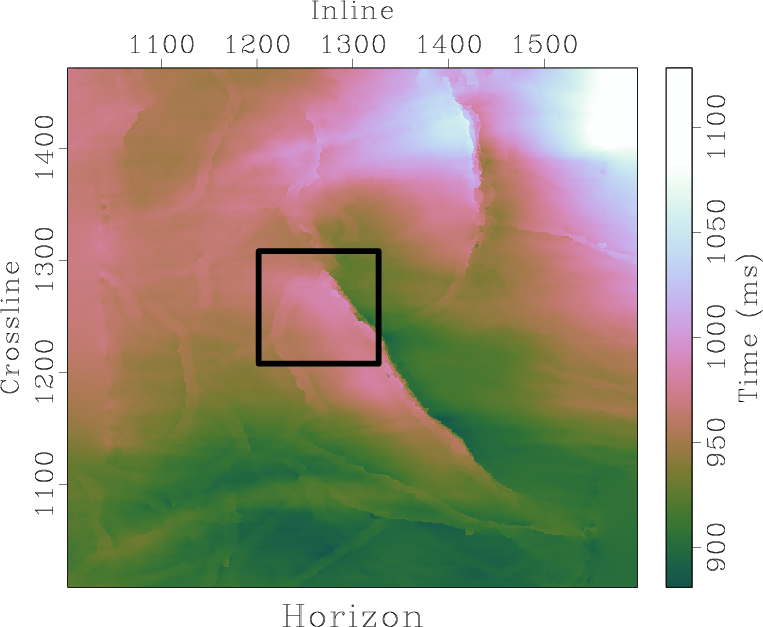
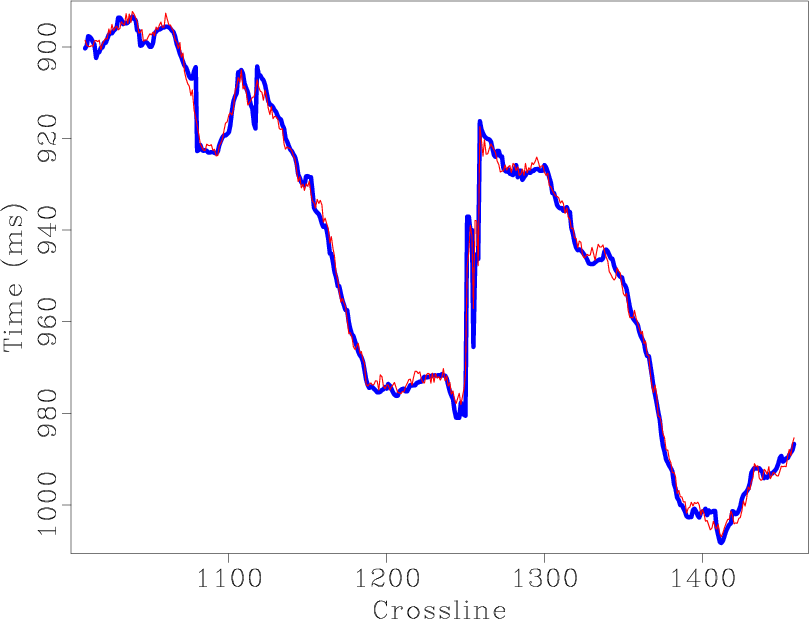
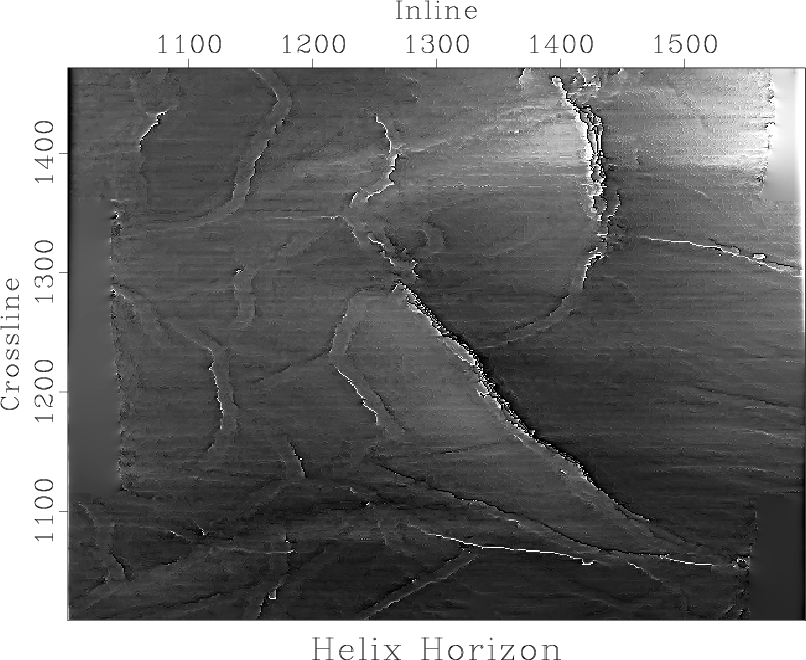
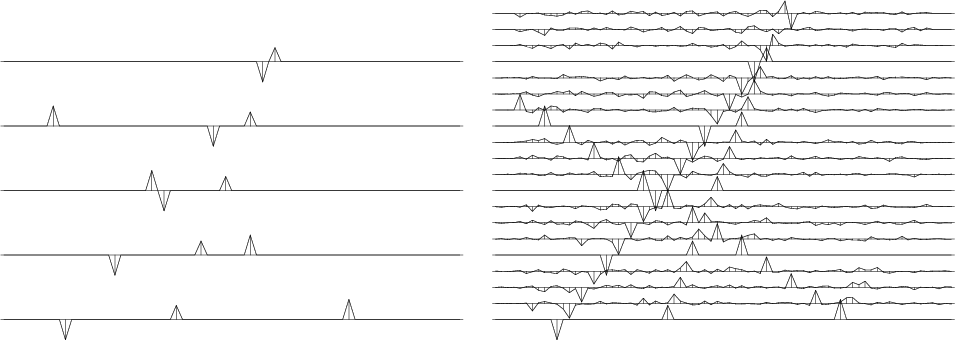
We present a method for selecting a migration aperture in Kirchhoff migration. We first split migrated data into constant-dip-angle partial images. Then, in every partial image, we estimate the consistency between each event and the constant dip of the analyzed section. We filter out events whose slope is far from the corresponding dip. Stacking of the filtered partial images corresponds to migration having an optimal aperture. Synthetic and real data examples demonstrate that the proposed approach to migration-aperture optimization is able to reduce migration noise while preserving diffraction energy, which characterizes small geological objects and brings additional resolution to the image.