|
|
|
|
Effects of lateral heterogeneity on time-domain processing parameters |
Next: Discussion Up: Diffraction traveltime in multilayer Previous: Layered anisotropic model with
In the final example, we consider a similar layered isotropic model with velocity gradient . Again, both effects from the curved reflectors (derivatives of 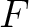 ) and the laterally varying slowness (derivatives of
) and the laterally varying slowness (derivatives of 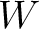 ) are important in this example. To ensure that the image ray is close to the reference vertical ray, we reduce the magnitude of the gradients to 30
) are important in this example. To ensure that the image ray is close to the reference vertical ray, we reduce the magnitude of the gradients to 30 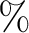 of the original values (Table 2).
of the original values (Table 2).
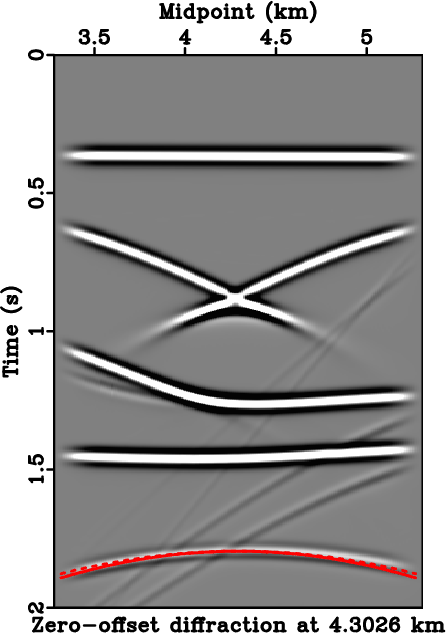
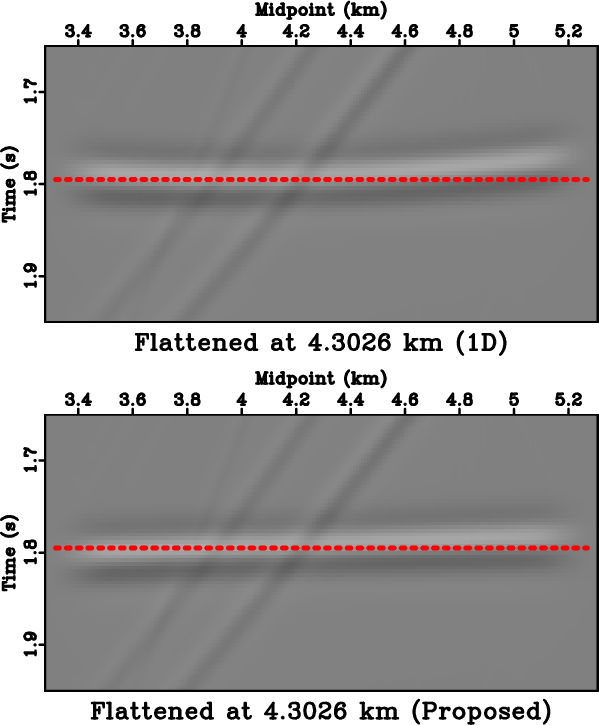
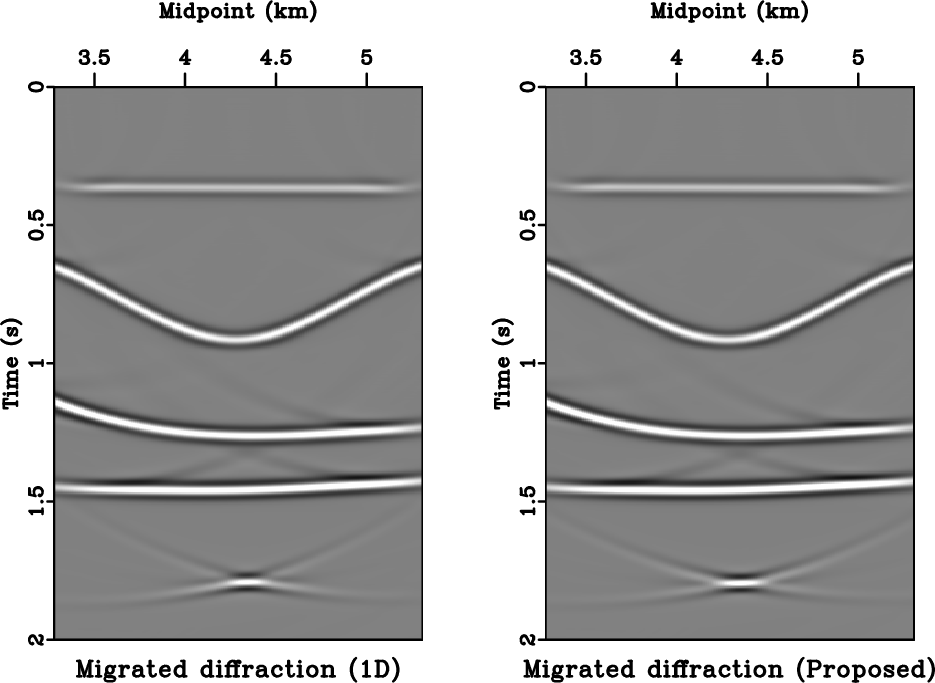
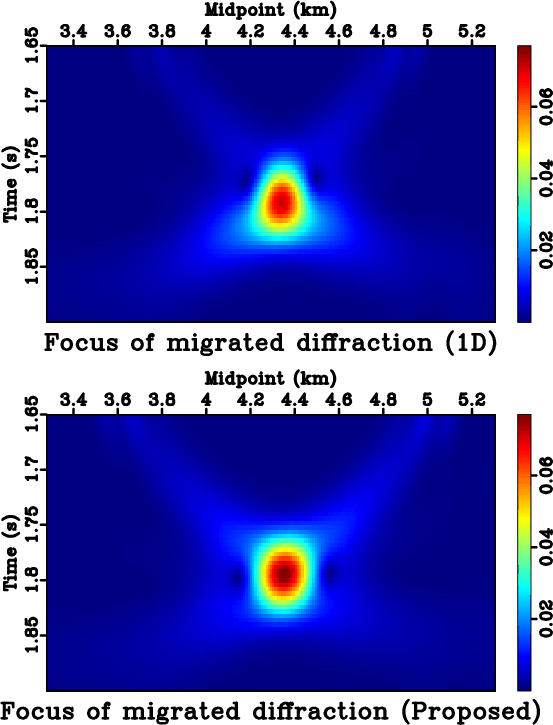
Figure 12a shows a zero-offset data around the point diffractor before migration overlain by two hyperbolic summation curves generated with migration velocities from the 1-D assumption and from the proposed method. The corresponding flattened diffraction travelime hyperbolas are shown in Figure 12b, which suggests a superior performance in traveltime prediction from the proposed method. Figure 13 shows the results from zero-offset Kirchhoff migration and Figure 14 shows their envelope focusing comparison. Similarly to the layered anisotropic case, we observe a superior diffraction response with higher and more symmetric focusing from the proposed method.
|
|---|
|
hypercomparediff3,warpedhypercompare3
Figure 12. An example zero-offset section from the layered isotropic model around 4.3 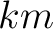 . The solid lines correspond to regular hyperbolic summation curve based on the assumption of 1-D stratified model, whereas the dashed lines correspond to that from the proposed framework that takes into account the effects from lateral heterogeneity. (b) Flattened diffraction events using the migration velocity with 1-D assumption (top) and the proposed framework (bottom). We can clearly observe improved flatness from using the proposed framework, which indicates a better traveltime prediction and in turn, a more focused migrated response. . The solid lines correspond to regular hyperbolic summation curve based on the assumption of 1-D stratified model, whereas the dashed lines correspond to that from the proposed framework that takes into account the effects from lateral heterogeneity. (b) Flattened diffraction events using the migration velocity with 1-D assumption (top) and the proposed framework (bottom). We can clearly observe improved flatness from using the proposed framework, which indicates a better traveltime prediction and in turn, a more focused migrated response.
|
|
|
|
|---|
|
migcompare
Figure 13. A zero-offset migrated section for the layered isotropic model. The resultant point diffractor appears to be better focused from the proposed method (right) than from the regular migration velocity based on 1-D assumption (left). |
|
|
|
|---|
|
envcompare
Figure 14. A focusing comparison of migrated point diffractors for the layered isotropic model. The proposed method leads to a higher magnitude of the central focusing at the center and a more symmetric response, which indicates its superior performance. |
|
|