|
|
|
|
Well log interpolation guided by geologic distance |
Next: Modified radial basis function Up: Method Previous: Method
Predictive painting (Fomel, 2010) spreads the time values along a reference trace into the seismic volume to output the relative geologic time (RGT) attribute.
Based on plane-wave destruction method (Fomel, 2002), the predictive painting operator
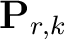 is a recursion of multiple operators that predict adjacent traces:
is a recursion of multiple operators that predict adjacent traces:
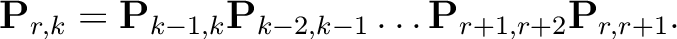 (1)
(1)
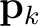 which are defined by plane-wave destruction.
which are defined by plane-wave destruction.
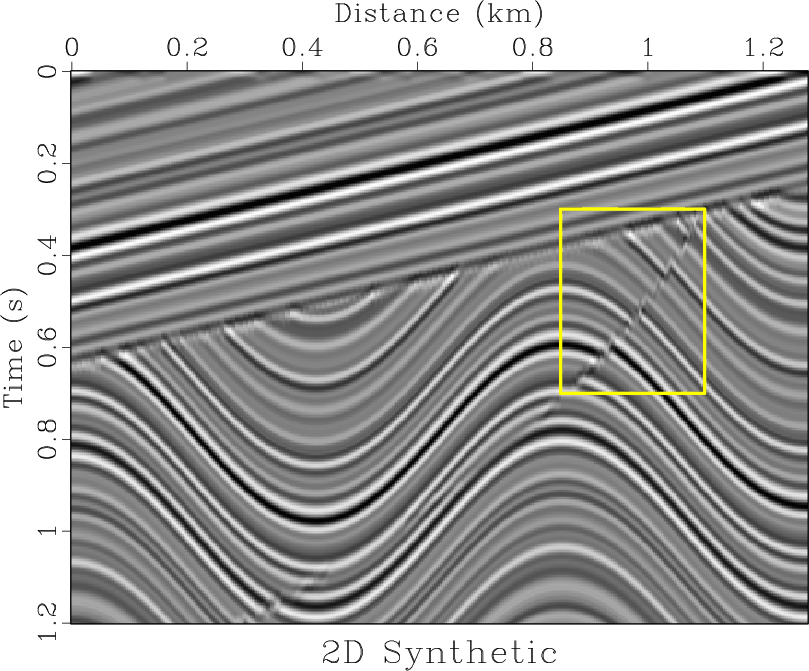
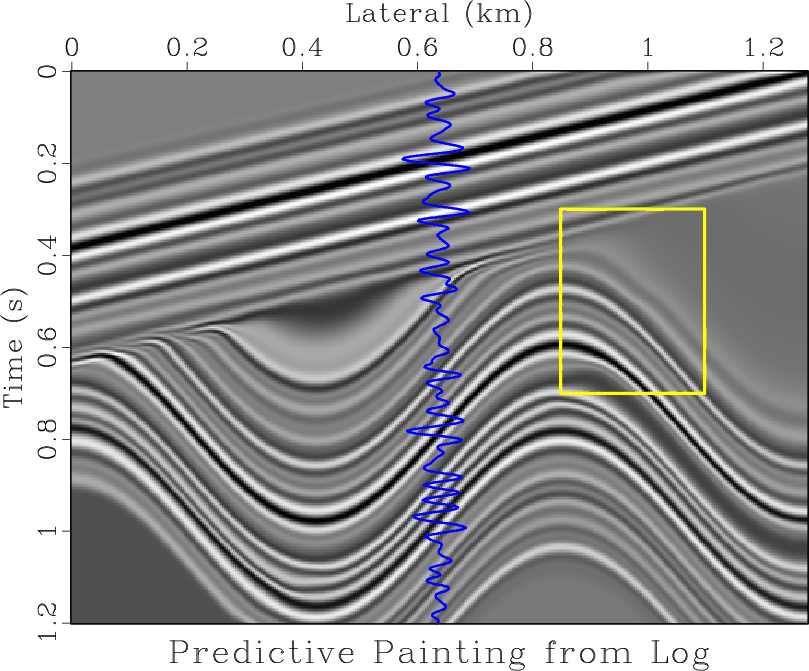
Figure 2 shows an application of predictive painting on the Sigmoid synthetic model (Claerbout, 1992) from Figure 1. While we use the seismic reflection signals to simulate the subsurface model, one of the seismic traces is extracted as a “well log” measurement. With proper sampling and ideal predictive painting based on the seismic image, we can recover the original model, which in this case is the same as the image itself.
|
|---|
|
sigmoid
Figure 1. Sigmoid synthetic model, including unconformities and faults. |
|
|
|
|---|
|
paint1
Figure 2. Predictive painting across the seismic image from synthetic well. The well-log synthetic is generated by copying the seismic trace at selected location. |
|
|
However, notice the fault highlighted by the box in Figure 1; predictive painting in Figure 2 failed to capture the discontinuities along seismic horizons.