 |
 |
 |
 | Time-shift imaging condition for converted waves |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Space- and time-shift imaging
Up: Imaging condition
Previous: Imaging condition
A conventional imaging condition for shot-record
migration, also known as
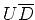 imaging condition (Claerbout, 1985),
consists of time cross-correlation at every image location
between the source and receiver wavefields,
followed by image extraction at zero time.
Mathematically, we can represent this process by the relations
imaging condition (Claerbout, 1985),
consists of time cross-correlation at every image location
between the source and receiver wavefields,
followed by image extraction at zero time.
Mathematically, we can represent this process by the relations
Here,
![${ \bf m}= \left[ m_x,m_y,m_z \right]$](img16.png) is a vector
describing the locations of image points,
is a vector
describing the locations of image points,
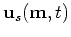 and
and
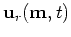 are source and receiver wavefields
respectively, and
are source and receiver wavefields
respectively, and
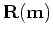 denotes the
migrated image, proportional to reflectivity at every location
in space.
The symbol
denotes the
migrated image, proportional to reflectivity at every location
in space.
The symbol 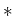 denotes cross-correlation in time.
denotes cross-correlation in time.
A typical implementation of this imaging condition is in the
Fourier domain, where the image is produced using the
expression
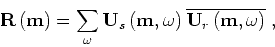 |
(3) |
where summation over frequency 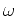 corresponds to imaging
at zero time.
The over-line represents a complex conjugate
applied on the receiver wavefield
corresponds to imaging
at zero time.
The over-line represents a complex conjugate
applied on the receiver wavefield 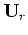 in the
Fourier domain.
in the
Fourier domain.
 |
 |
 |
 | Time-shift imaging condition for converted waves |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Space- and time-shift imaging
Up: Imaging condition
Previous: Imaging condition
2008-11-26