A new paper is added to the collection of reproducible documents: Dip-separated structural filtering using seislet transform and adaptive empirical mode decomposition based dip filter

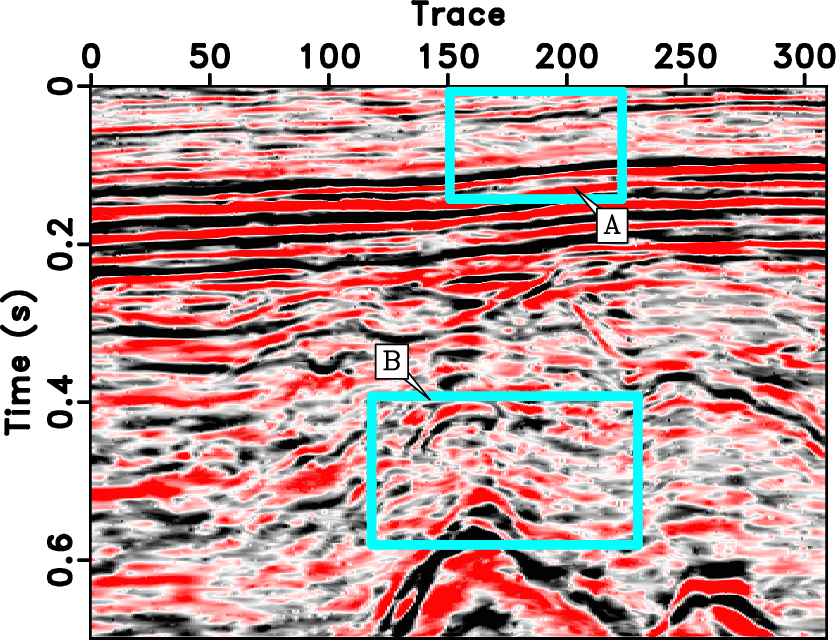
The seislet transform has been demonstrated to have a better compression performance for seismic data compared with other well-known sparsity promoting transforms, thus it can be used to remove random noise by simply applying a thresholding operator in the seislet domain. Since the seislet transform compresses the seismic data along the local structures, the seislet thresholding can be viewed as a simple structural filtering approach. Because of the dependence on a precise local slope estimation, the seislet transform usually suffers from low compression ratio and high reconstruction error for seismic profiles that have dip conflicts. In order to remove the limitation of seislet thresholding in dealing with conflicting-dip data, I propose a dip-separated filtering strategy. In this method, I first use an adaptive empirical mode decomposition based dip filter to separate the seismic data into several dip bands (5 or 6). Next, I apply seislet thresholding to each separated dip component to remove random noise. Then I combine all the denoised components to form the final denoised data. Compared with other dip filters, the empirical mode decomposition based dip filter is data-adaptive. Both complicated synthetic and field data examples show superior performance of my proposed approach than the traditional alternatives. The dip-separated structural filtering is not limited to seislet thresholding, and can also be extended to all those methods that require slope information.
codemore code
~~~~