 |
 |
 |
 | Fourier pseudo spectral method for attenuative simulation with fractional Laplacian |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Bibliography
Up: Fourier pseudo spectral method
Previous: Conclusion
.
One of the easiest absorbing boundary condtion (ABC) is sponge (or referred to as Gaussian taper) boundary condition proposed by [Cerjan et al.(1985)Cerjan, Kosloff, Kosloff, and
Reshef]. The principle is very simple: Attenuating the refections exponentially in the extended artificial boundary (Figure 2) area by multiplying a factor less 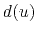 than 1, i.e.,
than 1, i.e.,
![$ d(u)=\mathrm{exp}(-[\alpha(nb-i)]^2), u=x,z (i\Delta x \; \mathrm{or} \; i\Delta z)$](img37.png) where
where 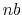 is the thickness of the artificial boundary on each side of the model. A usual choice is
is the thickness of the artificial boundary on each side of the model. A usual choice is
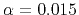 for
for
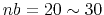 absorbing layers. The sponge ABC can be easily applied to a wide range of wave propagation problems, including some governing wave equations for complicated medium.
absorbing layers. The sponge ABC can be easily applied to a wide range of wave propagation problems, including some governing wave equations for complicated medium.
extbndrwidth=0.6A schematic diagram of extended artificial boundary area.
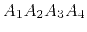 is the original model zone, which is extended to be
is the original model zone, which is extended to be
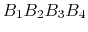 with artificial boundary. In the extended bounary area, the attenuation coeffcient
with artificial boundary. In the extended bounary area, the attenuation coeffcient
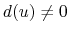 ; In the model zone
; In the model zone
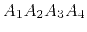 ,
, 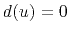 ,
, 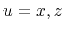 .
.
 |
 |
 |
 | Fourier pseudo spectral method for attenuative simulation with fractional Laplacian |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Bibliography
Up: Fourier pseudo spectral method
Previous: Conclusion
2021-08-31
![]() is the original model zone, which is extended to be
is the original model zone, which is extended to be
![]() with artificial boundary. In the extended bounary area, the attenuation coeffcient
with artificial boundary. In the extended bounary area, the attenuation coeffcient
![]() ; In the model zone
; In the model zone
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.